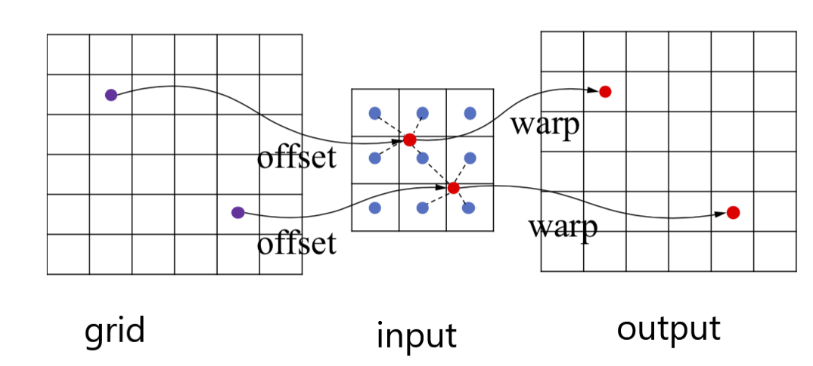
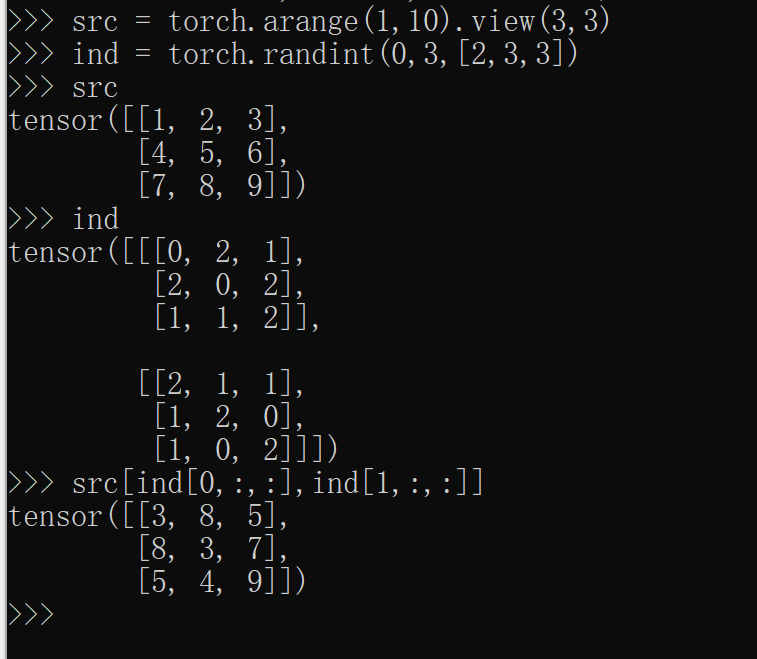
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
torch.eq(a,b)
torch.all(torch.eq(a,b))
>>> x = torch.arange(5)
>>> x
tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
>>> torch.gt(x,1)
tensor([0, 0, 1, 1, 1], dtype=torch.uint8)
>>> x>1
tensor([0, 0, 1, 1, 1], dtype=torch.uint8)
>>> torch.ne(x,1)
tensor([1, 0, 1, 1, 1], dtype=torch.uint8)
>>> x!=1
tensor([1, 0, 1, 1, 1], dtype=torch.uint8)
>>> torch.lt(x,3)
tensor([1, 1, 1, 0, 0], dtype=torch.uint8)
>>> x<3
tensor([1, 1, 1, 0, 0], dtype=torch.uint8)
>>> torch.eq(x,3)
tensor([0, 0, 0, 1, 0], dtype=torch.uint8)
>>> x==3
tensor([0, 0, 0, 1, 0], dtype=torch.uint8)
>>> torch.nonzero(x)
tensor([[1],
[2],
[3],
[4]])
>>> x = torch.Tensor([[0.6, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],[0.0, 0.4, 0.0, 0.0],[0.0, 0.0, 1.2, 0.0],[0.0, 0.0, 0.0,-0.4]])
>>> x
tensor([[ 0.6000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[ 0.0000, 0.4000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 1.2000, 0.0000],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.4000]])
>>> torch.nonzero(x)
tensor([[0, 0],
[1, 1],
[2, 2],
[3, 3]])
>>> x=torch.arange(12).view(3,4)
>>> x
tensor([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])
>>> (x>4).nonzero()
tensor([[1, 1],
[1, 2],
[1, 3],
[2, 0],
[2, 1],
[2, 2],
[2, 3]])
|